How to Measure Fork Offset – Detailed Guide?

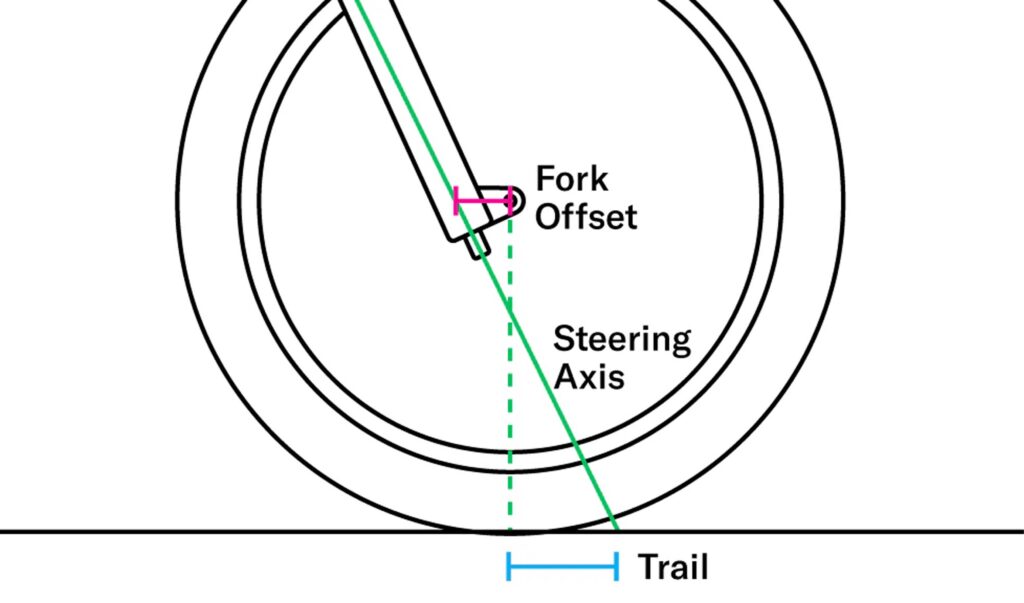
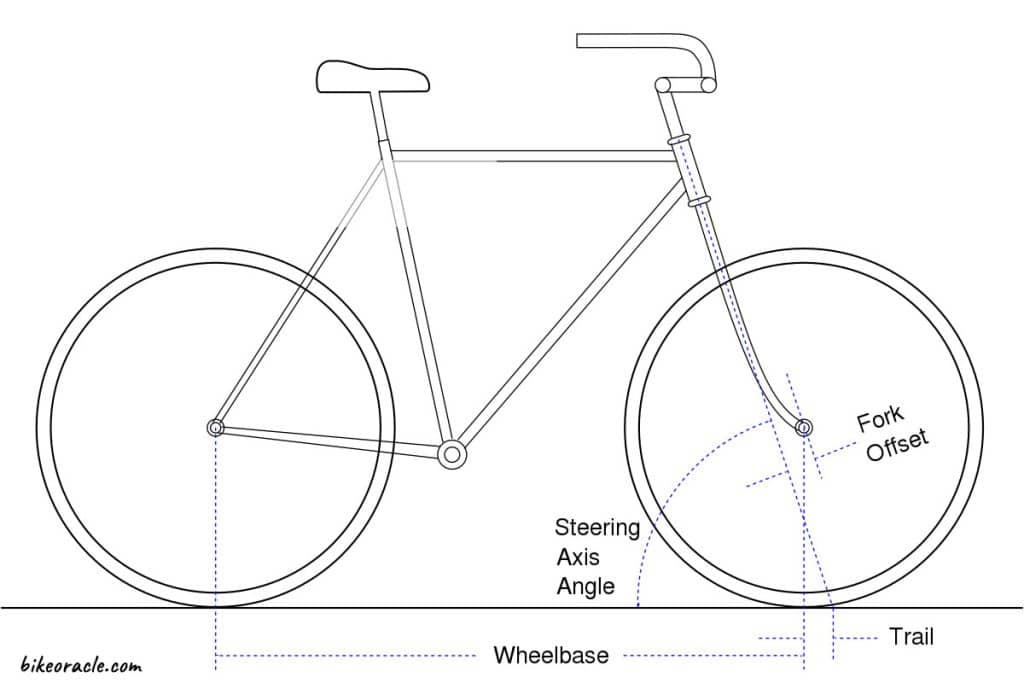
Fork offset denotes the horizontal gap between the steering axis and the center of the fork blades. By comprehending the intricacies of fork offset and its profound influence on bike performance, you gain the power to meticulously adjust your bike’s handling characteristics to perfectly align with your personal preferences and riding style. It’s a critical factor that empowers you to unlock the full potential of your bicycle’s performance.
Fork offset directly influences how a bike responds to steering inputs and maintains stability. A larger offset, or “rake,” provides a quicker steering response, making the bike more agile and suitable for tight turns. This is achieved by moving the front wheel forward, reducing the trail, and enhancing maneuverability. Cyclists who prioritize sharp cornering often choose a larger fork offset.
Conversely, a smaller fork offset contributes to greater stability, particularly during high-speed descents and straight-line riding. It achieves this by pushing the front wheel backward, increasing the trail. The elongated trail promotes self-centering steering and reduces sensitivity to small steering inputs. Cyclists who prioritize stability and long-distance rides may prefer a smaller fork offset.
Let’s walk you through a detailed, step-by-step guide for accurately measuring bike fork offset!
Bike Fork Offset: Understanding the Fundamentals
What is bike fork offset?
Basically, the distance between the centerline of a bike’s steering axis and the fork’s legs is a fork offset. It plays a crucial role in determining the handling characteristics of a bicycle. By adjusting the fork offset, the bike’s responsiveness and stability can be altered. It is an essential parameter to consider when fine-tuning a bike’s geometry for optimal performance.
Fork Offset vs. Rake and Trail: Clarifying the Distinctions
While fork offset influences a bike’s handling, it is distinct from rake and trail. Rake refers to the curvature of the fork blades, whereas trail is the horizontal distance between the contact point of the tire and the steering axis. Fork offset specifically focuses on the positioning of the fork legs relative to the steering axis, affecting the bike’s steering response and maneuverability.
Fork Offset and Bike Geometry: Understanding the Relationship
The fork offset is closely related to a bike’s overall geometry. A smaller fork offset tends to result in quicker and more responsive handling, ideal for nimble maneuvers and tight turns.
On the other hand, a larger fork offset provides greater stability and smoother steering, beneficial for high-speed descents and straight-line stability.
Achieving the desired balance between responsiveness and stability involves carefully considering the fork offset in conjunction with other geometry parameters.
Tools Required for Measuring Fork Offset
Overview of Necessary Tools
To accurately measure fork offset, you’ll need a few essential tools. Firstly, a ruler or measuring tape with millimeter markings is crucial for precise measurements. Additionally, a caliper or a fork offset gauge can provide more accurate results.
A torque wrench is also recommended for loosening and tightening the necessary bolts during the measurement process. Having these tools on hand will ensure a smooth and accurate measurement of fork offset.
The Importance of Accuracy in Measurement
Accurate measurement of fork offset is paramount for various reasons.
- Firstly, it helps ensure proper bike handling and stability, as the offset affects the bike’s steering characteristics.
- Secondly, accurate measurements allow for precise adjustments and compatibility when selecting new forks or components.
- Inaccurate measurements can lead to imbalanced weight distribution, poor bike performance, and potential safety issues.
Therefore, paying attention to accuracy when measuring fork offset is vital for optimal bike performance and rider safety.
Preparing the Bike for Measurement
Ensuring the bike is in a stable position
To obtain precise measurements when measuring fork offset, it’s crucial to properly prepare the bike. Here’s a guide on how to prepare your bike for accurate measurements:
Find a Level Surface
Begin by selecting a level and stable surface for the bike. It’s recommended to perform this task indoors or in a controlled environment where external factors are minimized. A flat surface ensures that the bike remains steady during the measurement process, preventing any disturbances that may affect the accuracy of the measurements.
Secure the Bike
To maintain stability and prevent the bike from tipping over, utilize a bike stand or securely prop the bike against a wall or another stable structure. This ensures that the bike remains upright throughout the measurement procedure, allowing for consistent and reliable measurements.
Check Tire Pressure
Before proceeding with the measurement, check the tire pressure and ensure that it complies with the manufacturer’s recommendations. Properly inflated tires are essential for maintaining consistent contact points with the ground. This consistency is crucial for obtaining accurate measurements of the fork offset. Verify the tire pressure to ensure optimal performance and reliable results.
By following these preparation steps, you create an environment that promotes accurate measurements. A level surface, secure bike positioning, and appropriate tire pressure contribute to the reliability of your measurements, enabling you to make informed decisions and adjustments for your bike setup.
Identifying the reference points for measurement
To measure various aspects of the bike accurately, it’s important to establish consistent reference points.
Here’s how to identify these reference points:
- Frame reference point: Determine a fixed reference point on the bike frame that serves as a baseline for measurements. This could be a specific location on the top tube, downtube, or any other rigid part of the frame.
- Wheel reference points: Identify specific reference points on the wheels, such as the center of the hub or the valve stem, which will be used to measure distances or assess wheel alignment.
- Component reference points: For measurements related to specific components, such as the handlebars, saddle height, or pedal position, establish clear reference points on those components. This ensures consistent measurements across different bikes and allows for accurate comparisons.
By establishing stable positioning and clear reference points, you can proceed with accurate measurements of the bike’s various dimensions and characteristics.
Measuring Fork Offset Step-by-Step
To obtain precise measurements when measuring fork offset, it’s crucial to properly prepare the bike. Here’s a guide on how to prepare your bike for accurate measurements:
Step 1: Find a Level Surface
Begin by selecting a level and stable surface for the bike. It’s recommended to perform this task indoors or in a controlled environment where external factors are minimized. A flat surface ensures that the bike remains steady during the measurement process, preventing any disturbances that may affect the accuracy of the measurements.
Step 2: Secure the Bike
To maintain stability and prevent the bike from tipping over, utilize a bike stand or securely prop the bike against a wall or another stable structure. This ensures that the bike remains upright throughout the measurement procedure, allowing for consistent and reliable measurements.
Step 3: Check Tire Pressure
Before proceeding with the measurement, check the tire pressure and ensure that it complies with the manufacturer’s recommendations. Properly inflated tires are essential for maintaining consistent contact points with the ground. This consistency is crucial for obtaining accurate measurements of the fork offset. Verify the tire pressure to ensure optimal performance and reliable results.
By following these preparation steps, you create an environment that promotes accurate measurements. A level surface, secure bike positioning, and appropriate tire pressure contribute to the reliability of your measurements, enabling you to make informed decisions and adjustments for your bike setup.
Alternative Methods of Measuring Fork Offset
Exploring alternative measurement techniques
When it comes to measuring fork offset, there are different methods to obtain accurate measurements. Let’s delve into a few of these techniques:
- Axle-to-Crown Measurement: By measuring the distance between the fork axle and the crown, and subtracting the distance from the crown race to the center of the axle, you can determine the fork offset. This widely used method provides precise measurements.
- Rake Measurement: Another approach is the rake measurement method. Rake refers to the distance between the steering axis (a line passing through the head tube and the fork’s centerline) and the contact point of the front wheel with the ground. By measuring the rake, you can indirectly determine the fork offset. This method requires careful measurement of the wheel’s contact point, which can be influenced by tire pressure and other factors.
- Visual Comparison: Visual comparison is a more subjective method where you visually assess the difference in fork offset by comparing two forks side by side. This method relies on your ability to detect variations in offset by observing the relative positioning of the fork legs. While it may provide a rough estimation, it is not as precise as the other measurement techniques mentioned.
Comparing the pros and cons of each method
Each alternative method of measuring fork offset has its own advantages and limitations. Let’s evaluate the pros and cons of each approach:
Axle-to-Crown Measurement
Pros:
- Provides a precise and direct measurement of fork offset.
- Relatively easy to perform with basic measuring tools.
- Offers accurate results for comparing different forks.
Cons:
- Requires accurate measurement of the crown race to axle distance.
- May be influenced by variations in crown race height or installation.
Rake Measurement
Pros:
- Allows for indirect determination of fork offset.
- Can be useful when direct measurement is not feasible.
- Offers a practical approach for assessing fork geometry.
Cons:
- Requires careful measurement of the wheel’s contact point.
- Subject to variations due to tire pressure and external factors.
- May not provide as precise results as the axle-to-crown method.
Visual Comparison
Pros:
- Quick and easy method for a rough estimation of fork offset.
- Useful for a visual assessment of offset differences.
Cons:
- Subjective and prone to human error.
- Less accurate compared to direct measurement techniques.
- Limited in providing precise numerical values.
Factors Affecting Fork Offset Measurement
Influence of Wheel Size on Measurement
With regards to estimating fork offset, the wheel size assumes a huge part in deciding the last estimation. The fork offset is the distance between the focal point of the fork’s steerer tube and the focal point of the fork’s dropouts, and it can fluctuate contingent upon the size of the wheel being utilized.
For instance, with bigger wheel sizes, for example, 29 inches, the fork offset will in general be more modest contrasted with more modest wheel sizes like 27.5 inches or 26 inches. This is on the grounds that bigger wheels by and large have a more extended contact fix with the ground, which influences the bicycle’s taking care of qualities. To maintain proper handling, the fork offset needs to be adjusted accordingly.
Impact of Suspension Travel on Fork Offset
Another factor that affects fork offset measurement is the suspension travel of the fork. Suspension travel refers to the maximum distance the fork can compress and extend, absorbing impacts from the terrain. Different forks have varying levels of suspension travel, and this can influence the fork offset.
Typically, forks with longer suspension travel tend to have a larger fork offset. This is because the increased travel requires more space for the fork to compress and extend without interfering with the bike’s frame and other components. On the other hand, forks with shorter suspension travel often have a smaller fork offset to maintain stability and proper handling characteristics.
Consideration of Tire Width when Measuring
When measuring fork offset, it’s important to consider the width of the tires that will be used with the fork. The tire width can affect the overall geometry of the bike and subsequently impact the fork offset measurement.
More extensive tires have a bigger contact fix with the ground, which can influence the bicycle’s security, ability to corner, and generally speaking taking care of. To oblige more extensive tires, the fork offset might need to be changed in accordance with guaranteed appropriate leeway between the tire and the fork legs. In some cases, forks specifically designed for wider tires may have a larger fork offset to accommodate the increased tire width.
It’s crucial to consider tire width when measuring fork offset to ensure optimal performance and compatibility between the fork, tire, and the rest of the bike’s components.
Interpreting Fork Offset Values
Understanding positive and negative fork offset
With regards to fork, offset esteems, it’s vital to embrace the ideas of positive and negative balances and what they mean for the exhibition and treatment of a bicycle. Positive fork offset alludes to the distance between the controlling hub of the fork and the centerline of the fork legs.
In less difficult terms, it decides how far forward the front wheel is situated corresponding to the directing hub. A larger positive offset pushes the front wheel further forward, resulting in increased trail and stability. This setup is commonly found on bikes designed for slower, more stable handling, such as touring or endurance bikes.
On the other hand, a negative fork offset means that the front wheel is positioned closer to the steering axis. This decreases the trail and makes the bike more responsive and nimble, ideal for quick maneuvering and agile handling. Bikes with negative offset forks are often seen in disciplines like mountain biking and cyclocross, where precise handling and quick cornering are crucial.
Exploring the effect of fork offset on bike handling characteristics
The fork offset plays a significant role in determining the handling characteristics of a bike. Let’s delve deeper into how different fork offset values can affect the bike’s performance:
Stability and High-Speed Handling:
- A larger positive fork offset increases stability by lengthening the trail, providing better straight-line stability and resistance to wheel flop.
- This setup is advantageous for long-distance riding, descents, and high-speed cruising, as it offers a more predictable and composed ride.
Agility and Low-Speed Maneuverability:
- Negative fork offset reduces trail length, making the bike nimbler and responsive, particularly at lower speeds.
- Bikes with negative offset forks excel in tight corners, technical terrain, and situations that require quick changes in direction.
Steering Sensitivity:
- Positive offset forks offer more relaxed steering, requiring less input to initiate turns and providing a stable feel.
- Negative offset forks enhance steering responsiveness, allowing for quicker and more immediate handling inputs.
It’s important to note that the ideal fork offset value varies depending on the bike’s intended use and personal preference. Factors like frame geometry, rider weight distribution, and riding style also come into play. Experimenting with different offset values can help fine-tune the bike’s handling to match specific riding preferences.
How to Adjust Fork Offset?
Overview of available adjustment options
With regards to changing fork offset, it’s fundamental to comprehend the accessible choices and what they can mean for your riding experience. Fork offset alludes to the distance between the centerline of the fork steerer tube and the centerline of the fork legs. By changing the fork offset, you can impact the bicycle’s dealing with attributes, steadiness, and responsiveness. Let’s explore the various adjustment options:
Standard Fork Offset
The standard fork offset is the default setting determined by the manufacturer. It is intended to give a reasonable and unsurprising ride, reasonable for most riders and riding styles. In the event that you haven’t made any changes in accordance with your fork offset, odds are you are now utilizing the standard setting.
Increase in Fork Offset
Expanding the fork offset lessens the path estimation, which alludes to the distance between where the controlling hub crosses the ground and the focal point of the front tire’s contact fix. This change can result in faster-taking care of, causing the bicycle to feel more responsive and dexterous. It is commonly preferred by riders who engage in technical and tight maneuvers, such as navigating tight corners or tackling steep descents.
Decrease in Fork Offset
Conversely, decreasing the fork offset increases the trail measurement. This change advances steadiness and works on the bicycle’s capacity to keep a straight line at high paces. It improves the bicycle’s general equilibrium and can help riders who focus on dependability over deft taking care of. This setting is often favored by riders who participate in downhill racing or prefer a more stable ride on rough terrain.
Discussing the potential impact of fork offset adjustment
Adjusting the fork offset can have significant implications for your bike’s performance and handling. Let’s explore the potential impact of fork offset adjustment:
Handling Characteristics
Altering the fork offset can affect how your bike handles various riding situations. Increasing the fork offset makes the bike more responsive, allowing for quick and precise steering inputs. This can be advantageous for technical maneuvers, sharp turns, or navigating obstacles. On the other hand, decreasing the fork offset enhances stability, making it ideal for high-speed descents or maintaining control on rough terrain.
Stability
Fork offset adjustment can directly impact the bike’s stability. Expanding the offset might bring about a somewhat less steady ride, particularly at higher paces, as the bicycle turns out to be more receptive to controlling sources of info. Diminishing the offset can upgrade security by working on the bicycle’s capacity to keep a straight line, settling on it an ideal decision for downhill riders or those looking for a more established feel.
Weight Distribution
Fork offset adjustments can influence weight distribution on the bike. Increasing the offset shifts the rider’s weight slightly forward, placing more load on the front wheel. This can improve traction and control in certain situations, such as steep climbs. Decreasing the offset redistributes weight towards the rear, which can be beneficial for stability and descending steep terrain.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Can the fork offset be adjusted on all bikes?
Yes, fork offset can be adjusted on most bikes, especially those equipped with adjustable forks. However, it’s important to consult your bike manufacturer’s specifications and guidelines to ensure compatibility and proper adjustment.
What is the ideal fork offset for different riding styles?
The ideal fork offset varies based on riding styles. For technical maneuvers and agility, increasing the offset is preferred. For stability and high-speed descents, decreasing the offset is recommended. It’s best to experiment and find what suits your riding style.
Is it possible to measure fork offset without removing the fork?
No, measuring fork offset requires removing the fork from the bike. It involves taking precise measurements between the fork steerer tube and the fork legs. Consulting a professional bike mechanic is recommended for accurate measurements and adjustments.
Conclusion
Measuring fork offset is a critical aspect of optimizing your electric bike’s performance. Fork offset, which refers to the distance between the steering axis and the fork’s blades, directly affects handling and stability. By accurately measuring and adjusting the fork offset, you can fine-tune your bike’s steering response and ensure precise cornering and control. It also impacts the bike’s trail, influencing stability across different speeds and terrains.
Take the necessary steps to adjust your bike’s fork offset for optimal performance. Refer to your bike’s manual or seek professional guidance to determine the appropriate measurement. Utilize accurate measuring tools and experiment with different settings to find the ideal fit for your riding style. Small adjustments can make a significant difference.
Don’t hesitate to seek expert advice or consult online resources for assistance. Optimizing your bike’s fork offset enhances responsiveness and overall enjoyment. Invest the time and effort for the best possible riding experience with your electric bike. Ride safe, ride smart, and make the necessary adjustments for an exceptional ride. Happy cycling!
![What Oil Can You Use On a Bike Chain – [Answered]](https://bikeoracle.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/08/What-Oil-Can-You-Use-On-a-Bike-Chain-768x512.png)




